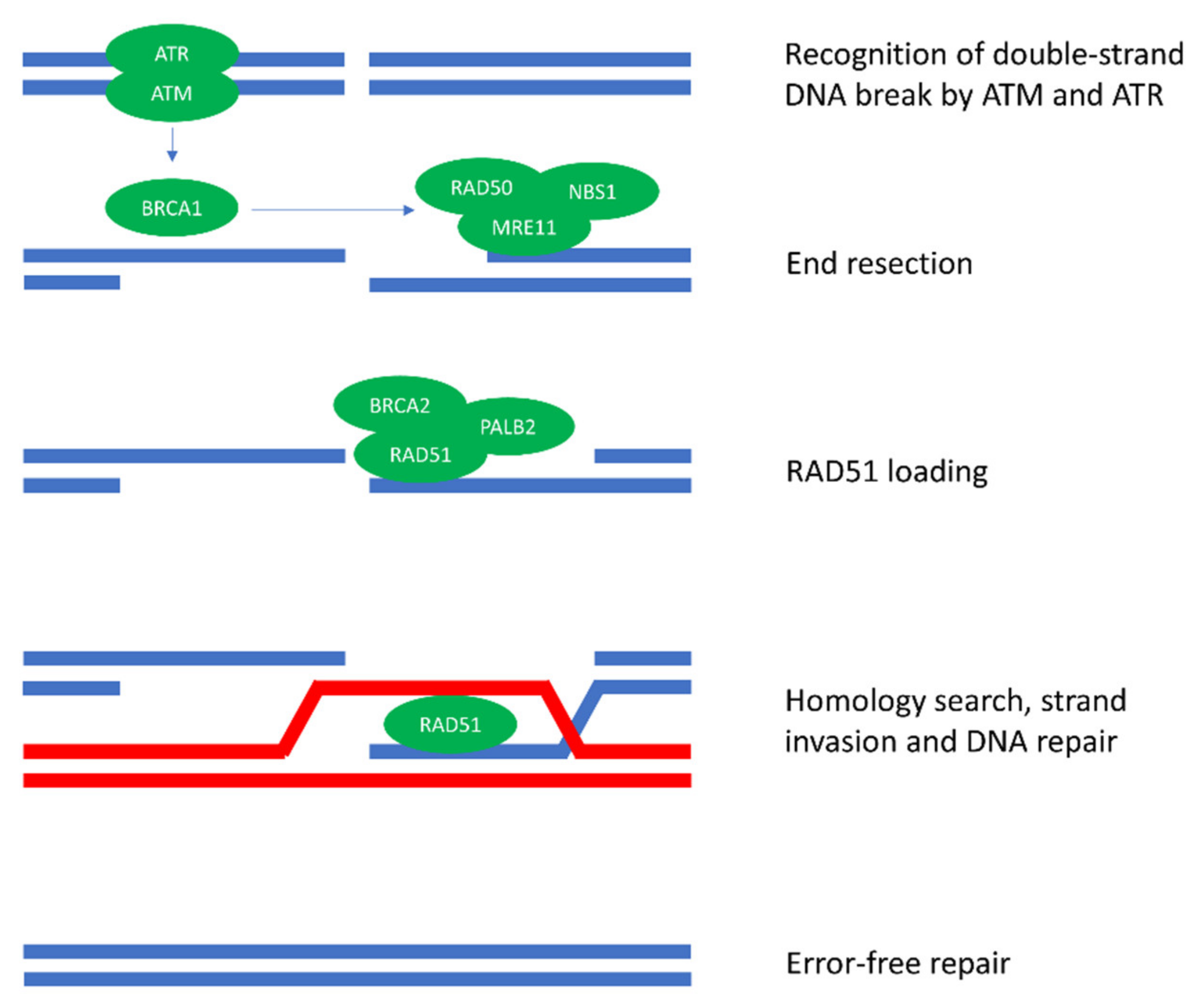
Homologous recombination Current Biology Biology Diagrams machinery, and recombination of a damaged DNA with its sister chromatid re-establishes the DNA replication fork3. Meiotic recombination is 100-1,000-fold more fre-quent than mitotic recombination, and it usually involves homologous chromosomes and generates chromosome-arm crossovers. These crossovers are essential for proper

Homologous recombination occurs in meiotic cells. In most species, every chromosome will undergo at least one recombination event. However, the ability to use one chromosome as a template for a broken one can also be used in instances of DNA damage, especially DNA backbone breaks. Remember that outside of meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are

PDF Mechanism of homologous recombination: mediators and helicases take on ... Biology Diagrams
Homologous recombination (HR) is an important mechanism for the repair of damaged chromosomes, for preventing the demise of damaged replication forks, and for several other aspects of chromosome

Learn about homologous recombination, the exchange of genetic material between two strands of DNA that contain long stretches of similar base sequences. Find out how it occurs naturally and in genetic engineering, and its role in DNA repair, meiosis, and evolution.

4.1.1: Homologous recombination Biology Diagrams
DNA Molecules Recombine by Breaking and Rejoining. Genetic recombination was first defined by studies of Drosophila, on the basis of the observation that genes on different copies of homologous chromosomes can reassort during meiosis.With the subsequent discovery that genes consist of DNA, two alternative models to explain recombination at the molecular level were considered (Figure 5.28).